ONE ISLAND - TWO FACES
Hispaniola
Caribbean Paradise
Hispaniola is the 22nd-largest island in the world, located in the Caribbean island group, the Greater Antilles. It is the second largest island in the Caribbean after Cuba, and the tenth most populous island in the world.
Hispaniola is the site of the first permanent European settlement in the Americas, founded by Christopher Columbus on his voyages in 1492 and 1493.



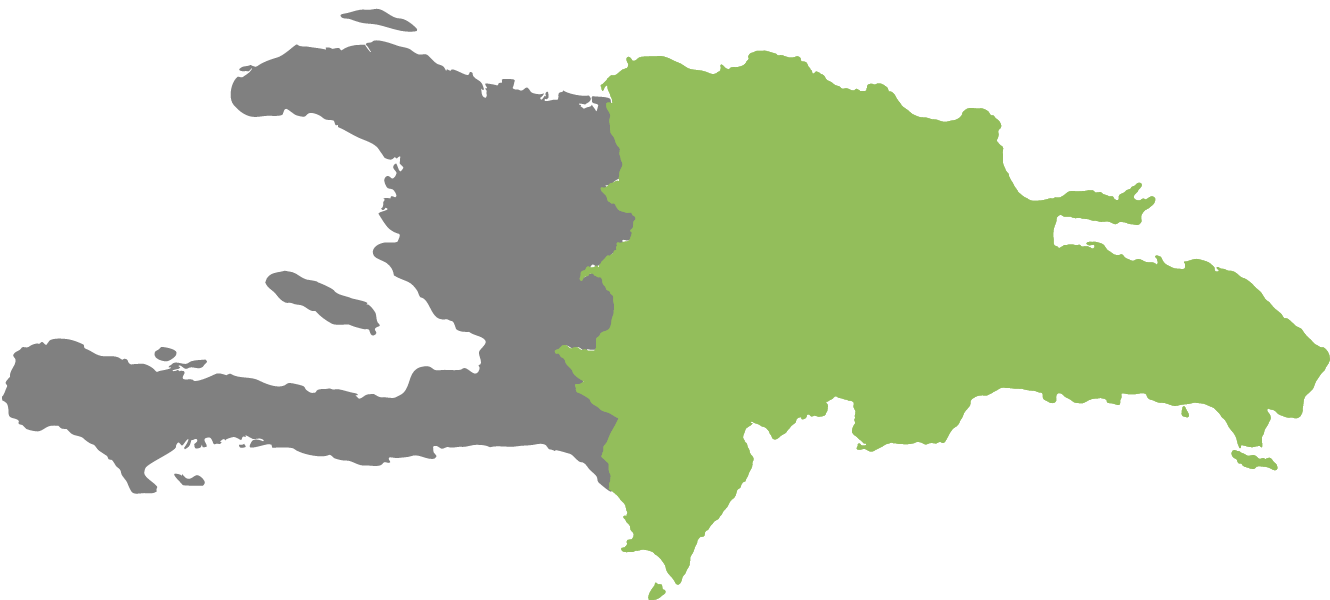
Geography
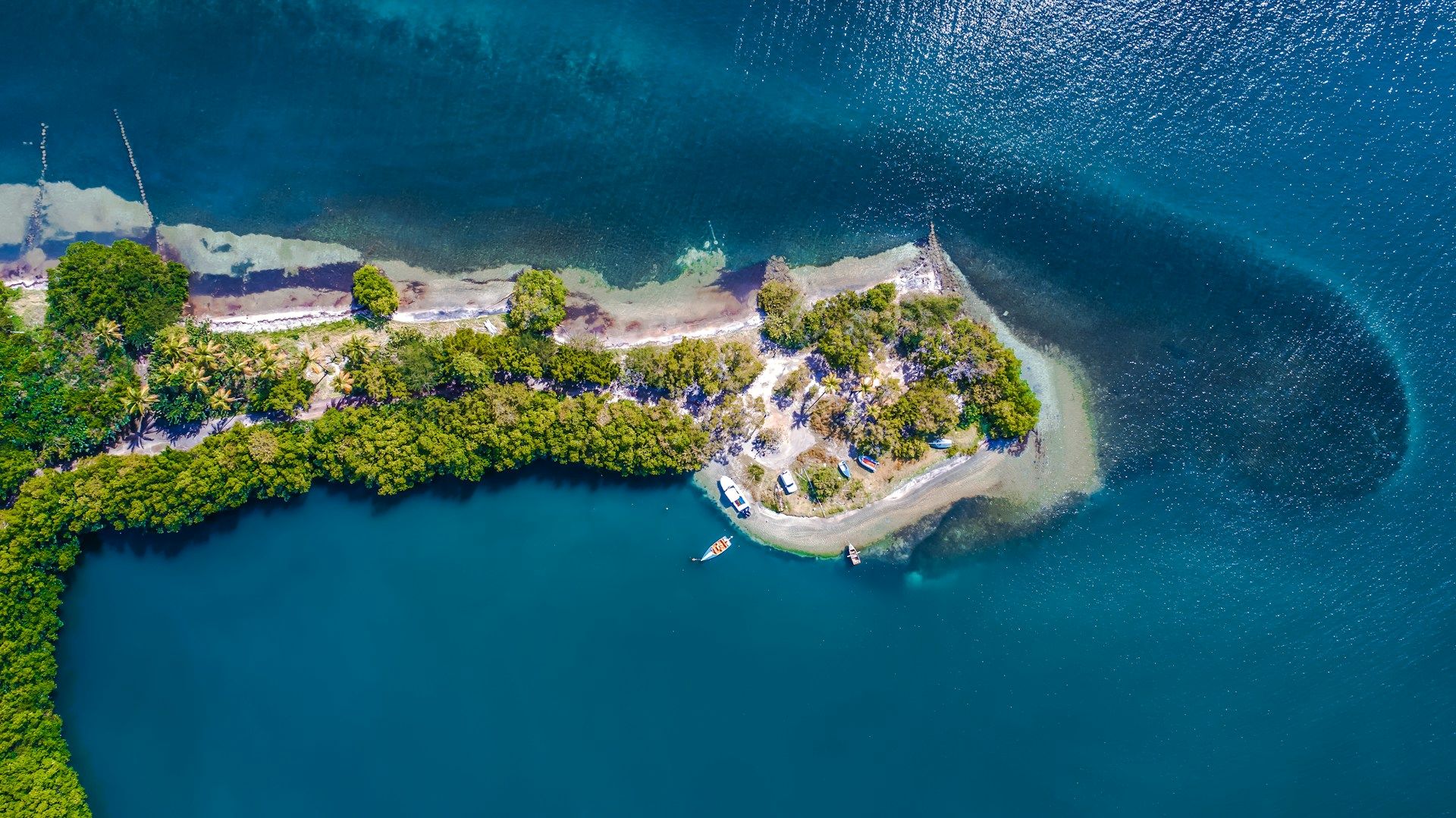
Hispaniola is the second largest island of the West Indies, with an area of about 76,126 km². The name given to the island was Columbus. Hispaniola means "small Spain". The Tainos called the island "Quisqueya", Mother Earth.
From a geological point of view, the island of Hispaniola is part of two branches of the North American cordillera system and is about 660 km long, 250 km wide and extends west-easterly. In the west, the island of Hispaniola is separated by the approximately 90 km wide Windward Passage from Cuba and in the east by the Mona Passage from Puerto Rico, which is up to 110 km wide.
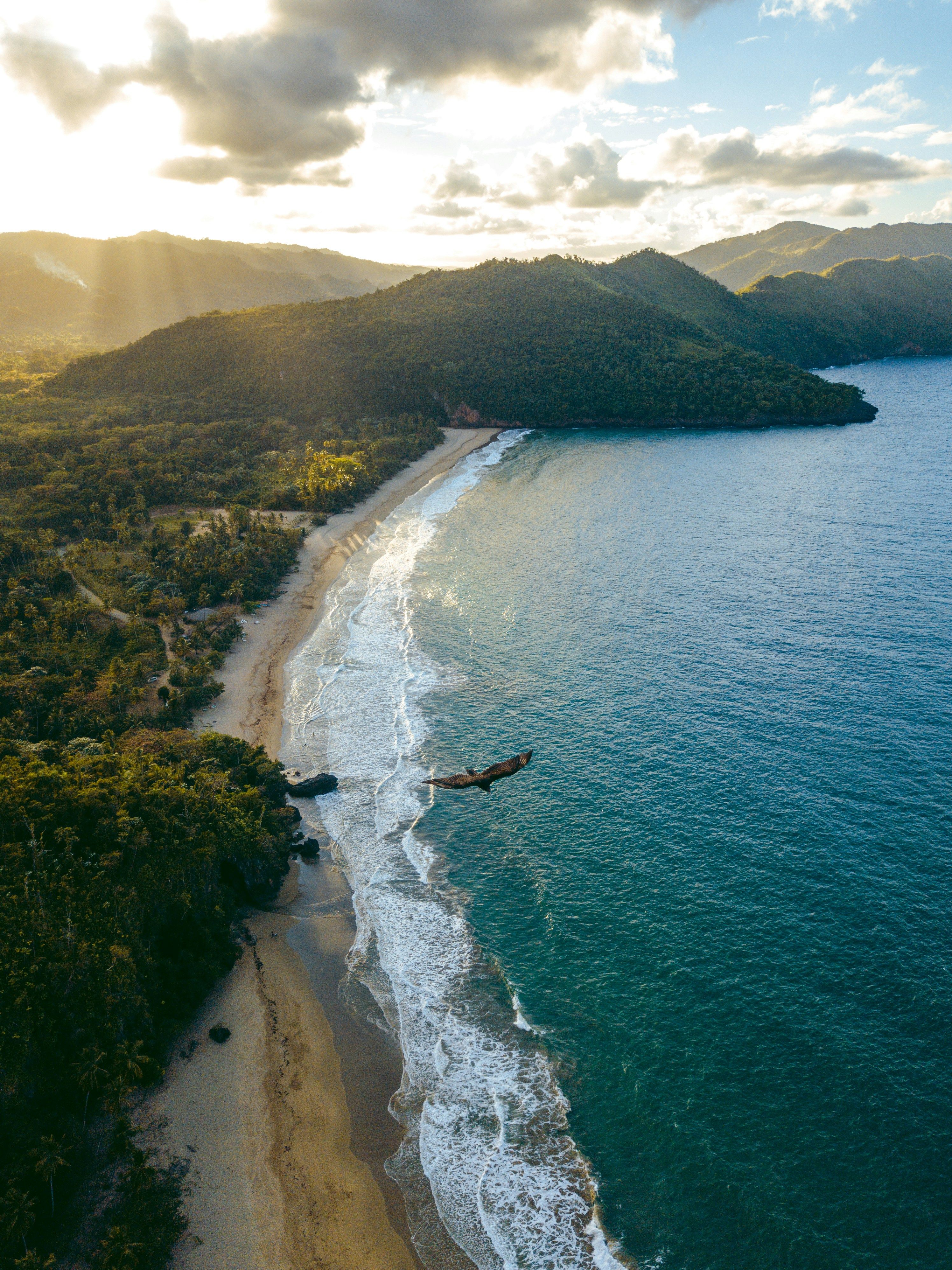
On the island of Hispaniola lie five large mountain chains. The highest mountains of the Caribbean are in the Dominican Republic. The highest mountain is in Pico Duarte with 3098 meters above sea level. Also the deepest point of the Caribbean lies on Hispaniola: the salt lake Enriquillo in the southwest of the Dominican Republic.
Hispaniola offers four vegetation zones and five climatic zones. More than 5000 plant species, many of the endemic, make the island a paradise for nature lovers. The animal world is also convincing, although it is not possible to affect large animals except for a few species. For this, the bird world is represented even more arsenically.
History
The island of Hispaniola (La Isla Espanola) was the first colony in the New World settled by Spain.
As such, it served as a logistical base for the conquest of most of the Western Hemisphere. Christopher Columbus first sighted the island in 1492 toward the end of his first voyage to "the Indies".
For two centuries the Spanish ruled the island until western Hispaniola (present-day Haiti) came under French control in 1697. The ease still remained under Spanish control. This created a division that still exists today, with the Dominican Republic and Haiti sharing the island.
Finally, and after the decades of unstable political situations, on 27 February 1844, the territory of Santo Domingo recovered its sovereignty and declared its independence as the Dominican Republic.
What to see and what to do!
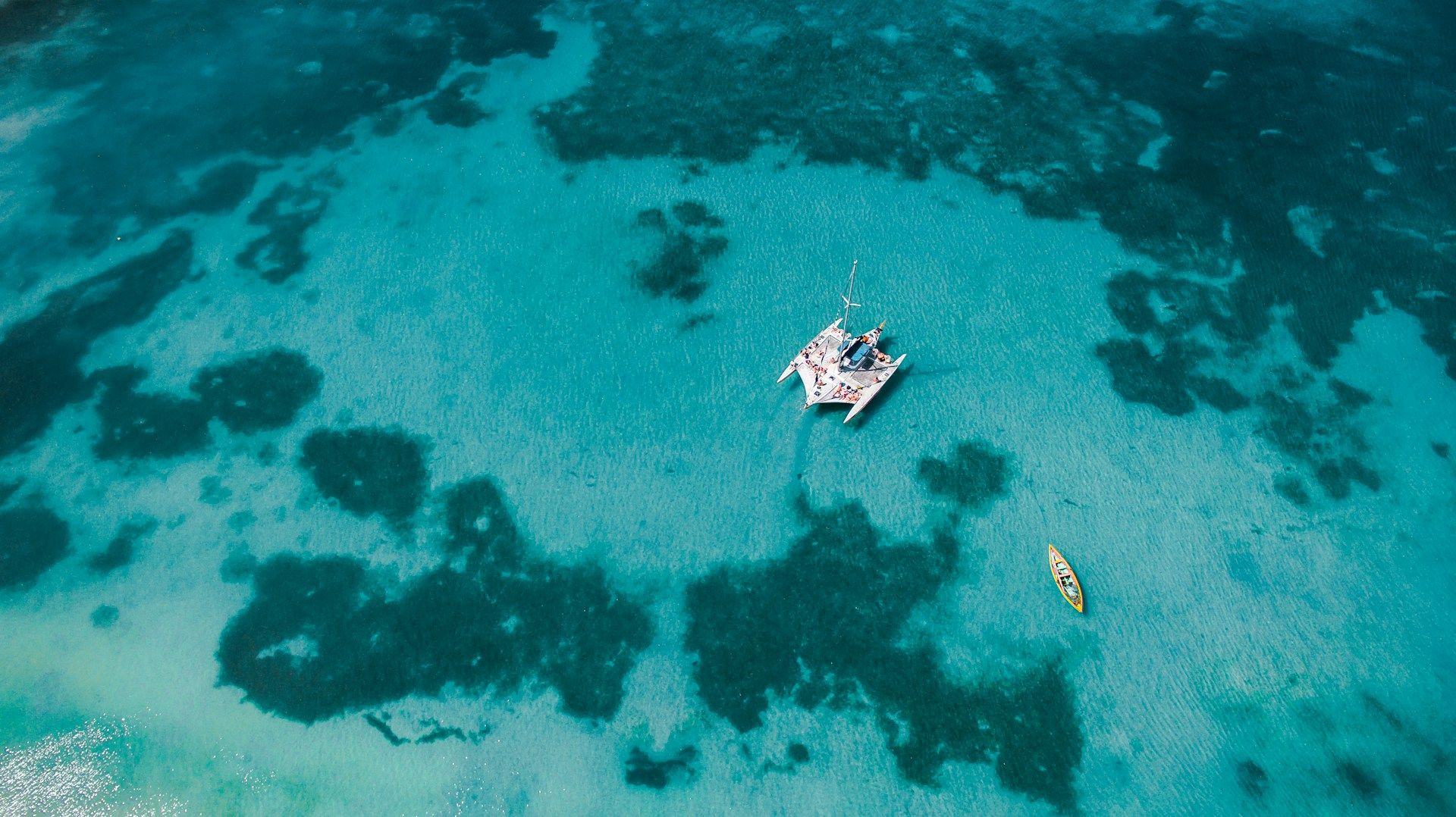
Wild mountain streams, hidden caves and dreamy waterfalls can be visited on guided tours in the mountains. Walks through tropical mountain forests, biking at the beaches and safaris for bird and bird watching are just a few of the recommendations that we can give you.
Discover the original southwest of the Dominican Republic and Haiti with Ecotour Barahona.

